Welding equipment and metal stamping parts
2. Electrical Connectivity - Energy Channels
The core of welding is high current (tens to hundreds of amperes). Ordinary wires are inconvenient to connect inside the machine and take up space, while stamped parts provide a better solution.
Busbars:
Function: Connect the output terminal of the transformer and the output terminal, carrying a huge welding current.
Process: Made by stamping and bending thick copper or aluminum plates. Compared to cables, stamped copper bars have better heat dissipation, more compact structure, and lower resistance.
Earth Clamps:
Function: Clamp on the workpiece to form a circuit.
Process: The main body of the strong clamp is usually stamped from galvanized steel plate, and the conductive contact pieces inside are copper stamped parts. Stamping springs ensure clamping force.
Terminal block: The connecting piece between the internal circuit board and the power device.
3. Wire Feeding Mechanism - The Key to MIG/MAG Welding Machines
In gas shielded welding (double shielded welding), the welding wire needs to be smoothly fed out.
Pressure Arm:
Function: Press the welding wire onto the wire feeding wheel.
Craftsmanship: This is a lever structure that is subjected to force, usually made by stamping thick steel plates to ensure long-term use without deformation.
Gears and brackets:
The gear and motor fixing brackets of some small wire feeders are precision stamped parts.
4. Torch & Electrode Holder Parts
The operating tool held by the welder also has stamped parts inside.
Electrode Holder:
Function: Clamp welding rod (manual arc welding).
Craftsmanship: Internal springs, lever drive plates, and metal lining for protecting the handle.
Trigger:
Function: Control the start/stop of welding.
Craftsmanship: The internal micro shrapnel (phosphor copper) requires extremely high fatigue life and cannot fail after tens of thousands of presses.
5. Thermal Management
Fan bracket: a metal frame used to secure a powerful cooling fan.
Heat sink fastener: A metal spring or pressure strip that presses IGBT/MOSFET onto an aluminum heat sink.
6. Safety Gear
Headband adjustment mechanism: The automatic dimming mask is equipped with an adjustment ring on the head, and its internal ratchet structure and positioning spring are usually micro stamped parts.
Why welding equipment cannot do without stamped parts?
Durable and sturdy: Welding machines are often moved around and even hit. The plastic shell is prone to breakage, while the steel plate stamped shell is only concave and does not affect its use.
EMC: As mentioned earlier, only a stamped all metal shell can effectively shield the high-frequency interference generated by welding, ensuring stable operation of the equipment.
Heat resistance: The temperature in the welding area is extremely high, and splashing welding slag (hundreds or thousands of degrees) will melt when it falls on plastic, but it will be fine when it falls on metal stamping parts.
Cost control: Whether it's a household welding machine costing a few hundred yuan or an industrial welding machine costing tens of thousands of yuan, stamping technology can provide structural and conductive components at the lowest cost.
summary
In welding equipment, metal stamping parts mainly play the roles of "armor" (shell shielding and protection) and "blood vessels" (copper bars transmitting high currents). They ensure that welding machines can safely and stably output powerful energy even in harsh industrial environments.
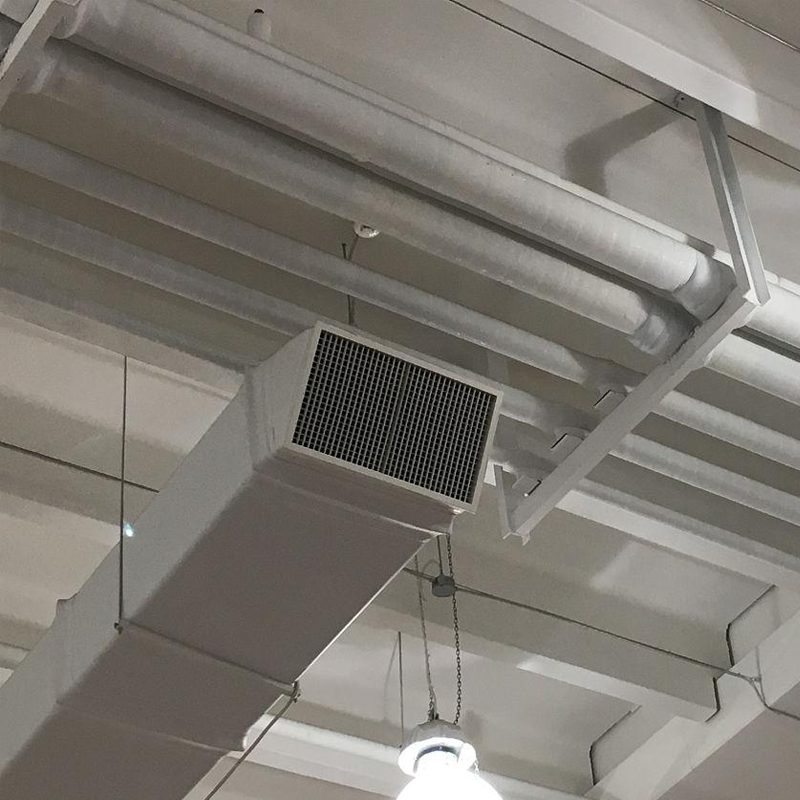 Ventilation systems and metal stamping parts
Ventilation systems and metal stamping parts
 Automotive and metal stamping parts
Automotive and metal stamping parts
 Cables and metal stamping parts
Cables and metal stamping parts
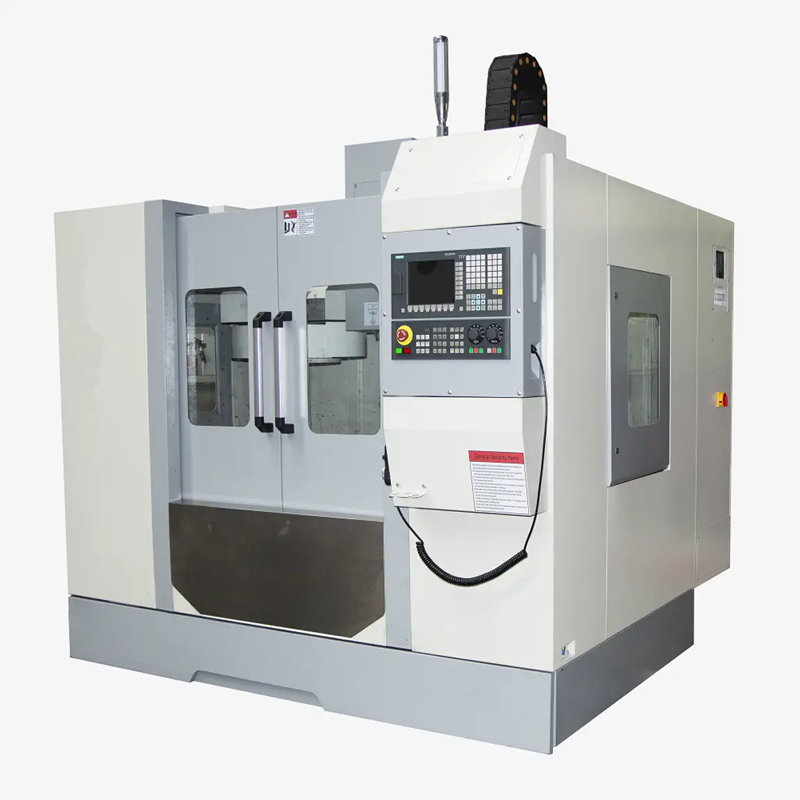 Numerical control equipment and metal stamping parts
Numerical control equipment and metal stamping parts

